Starting the Linked List
To build a linked list we need to start with a struct that can be used to manage the list itself. This will contain a pointer to the start of the list, and another pointer that refers to the end of the list. The pointer to the start can be used when we need to access the nodes of the list, this tells us where to start. The pointer to the last node can be used when we want to add a new node to the end of the list.
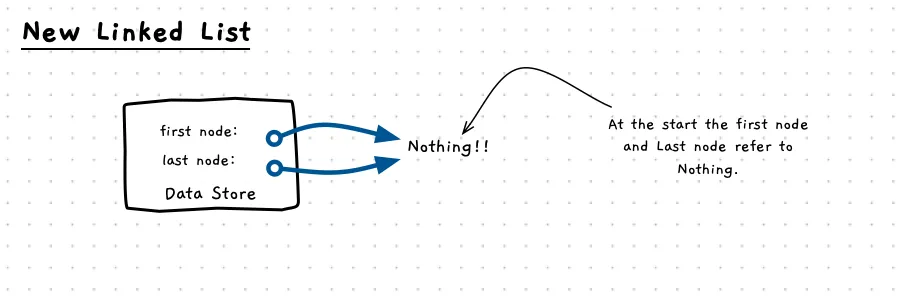
When we start a new list, the start and end pointers both need to point to nothing (NULL) as shown in the following image. With the linked list, the NULL indicates there is no node at this location.
To build this we will need to create a struct for the node, and a struct for the linked list. Once again, this is something that Copilot has seen many times. So it can help us get this going.
Here are the comments I used as prompts for Copilot, and the code after I cleaned it up a litte.
#include <stdlib.h>
/** * A node is a struct that contains a pointer to the next node, * and a data value. * * @tparam T The type of the data that will be stored in the node. * @field next A pointer to the next node in the list. * @field data The data that is stored in the node. */template <typename T>struct node { node *next; T data;};
/** * A linked list is a struct that contains a pointer to the * first node, and the last node of the list. * * @tparam T The type of the data that will be stored in the list. * @field first A pointer to the first node in the list. * @field last A pointer to the last node in the list. */template <typename T>struct linked_list { node<T> *first; node<T> *last;};Creating a new linked list
With this in place Copilot picked up that I probably wanted a new_linked_list function next. The suggestion even added the comments. If not, then you can add prompts to get it going in the right direction.
/** * Creates a new linked list. * * @tparam T The type of the data that will be stored in the list. * @return A pointer to the new linked list. */template <typename T>linked_list<T> *new_linked_list(){ linked_list<T> *list = (linked_list<T> *) malloc(sizeof(linked_list<T>)); list->first = NULL; list->last = NULL; return list;}