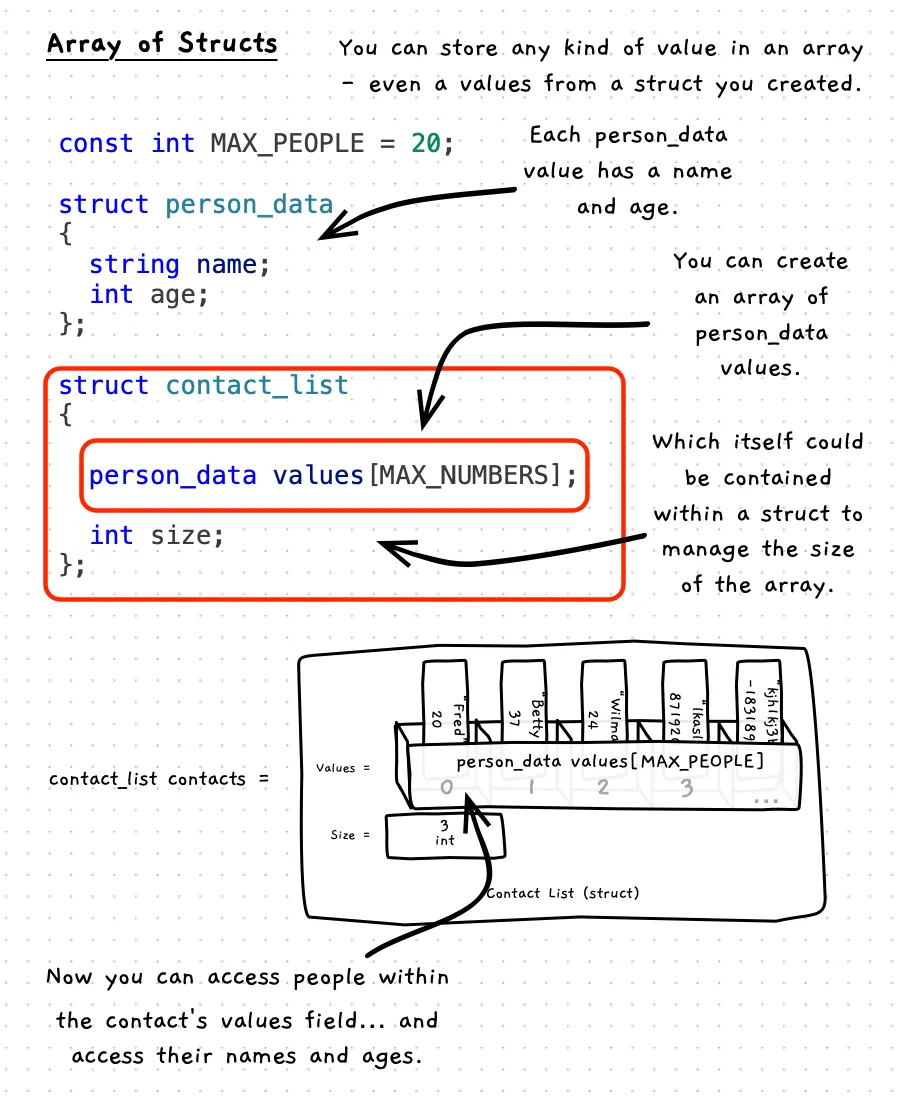
Struct with Array
One effective way to work with arrays is to place the array and its size into a struct. This allows you to keep the data and the number of elements that is has nicely together. You can then also use the size to give you the capability of adjusting the number of elements you are using, by changing the value of the array’s size. With this, you can then grow and shrink the size of the array, up to a set maximum number of elements.
The following illustrates the code and how to think about a struct that contains an array:
Example
#include <cstdio>#include "utilities.h"
// The maximum number of values we can storeconst int MAX_NUMBERS = 20;
/** * The data structure to store the numbers * * @field values the array of values * @field size the number of values in the array - up to MAX_NUMBERS */struct number_data{ double values[MAX_NUMBERS]; int size;};
int main(){ // Initialise struct with an empty array and a size of 0. number_data data = {{},0};
// You can pass to a procedure by reference, and have it update populate_array(data);
data.values[0] = read_double("Enter a value: "); data.size = 1;
data.values[1] = read_double("Enter a value: "); data.size = 2;
printf("Size is %d\n", data.size); printf("Element 1 is %lf\n", data.values[0]);
return 0;}