Design and Code Play Game
We are almost at a fully functional game. We can now put aside the perform guess code - we have it working, so you do not need to focus on how it works now. Instead, you can focus your attention on the next function or procedure: play game.
Play game will be responsible for coordinating the actions of the game, while perform guess coordinates the actions for a single guess. The following table captures a specification for this procedure.
| Procedure | Play Game |
| Description | Play game is responsible for coordinating the actions involved in playing a single game of Guess that Number. Initially the computer will generate a random target value, and output starting text. Then it will repeatedly ask the user to guess the number, until either the user has guessed the value or they have run out of guesses. If the user does run out of guesses then the computer ends the game, and tells the user the target value. |
Play Game procedureTo start let’s update our code to add in this play game procedure.
#include "splashkit.h"
// add read string, read integer, and read integer range here
// add perform guess here
// start play game here - you can copy in the old code from main
int main(){ play_game(); return 0;}- /*** Implements a simple guessing game. The program generate* a random number, and the player tries to guess it.*/void play_game(){while ( ! perform_guess(1, 37) ){write_line("Try again...");}}
Data for play game
The implementation of this procedure will require us to store some data. I think the following local variables will be needed:
My Number: This will store the computer’s randomly chosen number.Guess Number: This will store the current guess the user is at, allowing the computer to stop looping when the number of guesses exceeds 7.Got It: A Boolean value to indicate if the user did guess the number, allowing the computer to stop looping when the user guesses the number.
The flowchart below shows the logic for play game. This has a loop to ask the user to perform up to 7 guesses. The condition on this loop occurs after the loop body as the user must have at least one guess - so we can use a do while loop.
There is also a selection after the loop to output the answer if the user ran out of guesses. This is only done when the user has not guessed it themselves. This does not need to perform any other actions when the user did guess the number, so the false branch is empty. We added got it as a variable so that we can do this, otherwise we could have just used perform guess in the condition as we did when we were testing it.
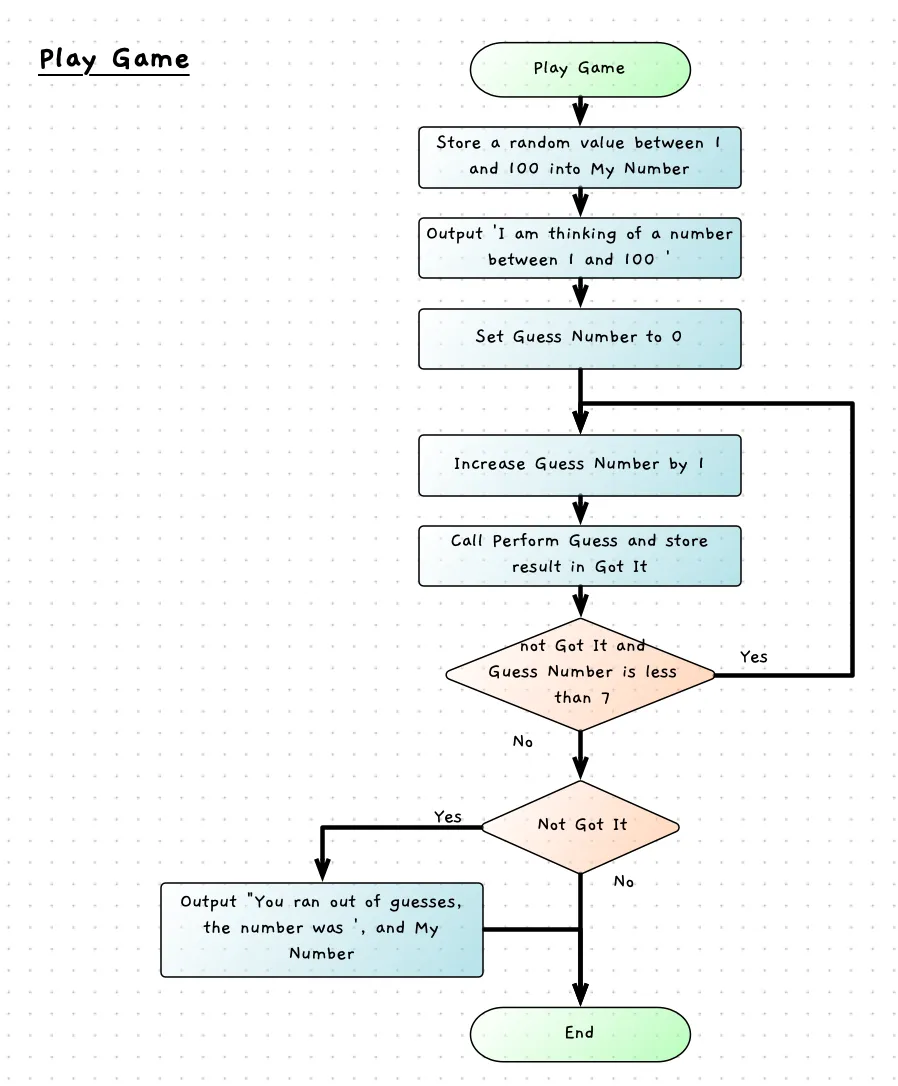
We can also express this in pesudecode as:
Procedure: Play Game-------------------------------Constants: - MAX_GUESSES: an integer with value 7 - MAX_NUMBER: an integer with value 100Local Variables: - My Number, Guess Number (Integer) - Got It (Boolean)Steps Assign My Number, a Random number between 1 and MAX_NUMBER Assign to Guess Number, the value 0 Output 'I am thinking of a number between 1 and ', and MAX_NUMBER Repeat Increase Guess Number by 1 Assign Got It, the result of PerformGuess(Guess Number, My Number) While Guess Number < MAX_GUESSES and not Got It If Not Got It then Output 'You ran out of guesses... the number was ', and My NumberHave a go at coding this yourself now. To generate the random number we can use SplashKit’s rnd function. You can pass this a min and a max, and it will return a random number between those values.
-
To make this neater, I introduced two constants for the maximum number and the maximum number of guesses.
const int MAX_NUMBER = 100;const int MAX_GUESSES = 7;/*** Implements a simple guessing game. The program generate* a random number, and the player tries to guess it.*/void play_game(){int my_number, guess_number;bool got_it;my_number = rnd(1, MAX_NUMBER);guess_number = 0; // Keep track of the number of guesseswrite_line("I am thinking of a number between 1 and " + to_string(MAX_NUMBER) + "\n");do{guess_number++;got_it = perform_guess(guess_number, my_number);} while (guess_number < MAX_GUESSES && !got_it);if (!got_it){write_line("You ran out of guesses... the number was " + to_string(my_number) + "\n");}}
Test it out
Give your game a go. Can you guess the value within the 7 guesses?