Local Variable
Functions and procedures create new spaces within our code. Variables created within a function or procedure are called local variables. They live within the function or procedure, can only be accessed by the function or procedure’s code, and are removed from memory when the function or procedure ends.
Examples
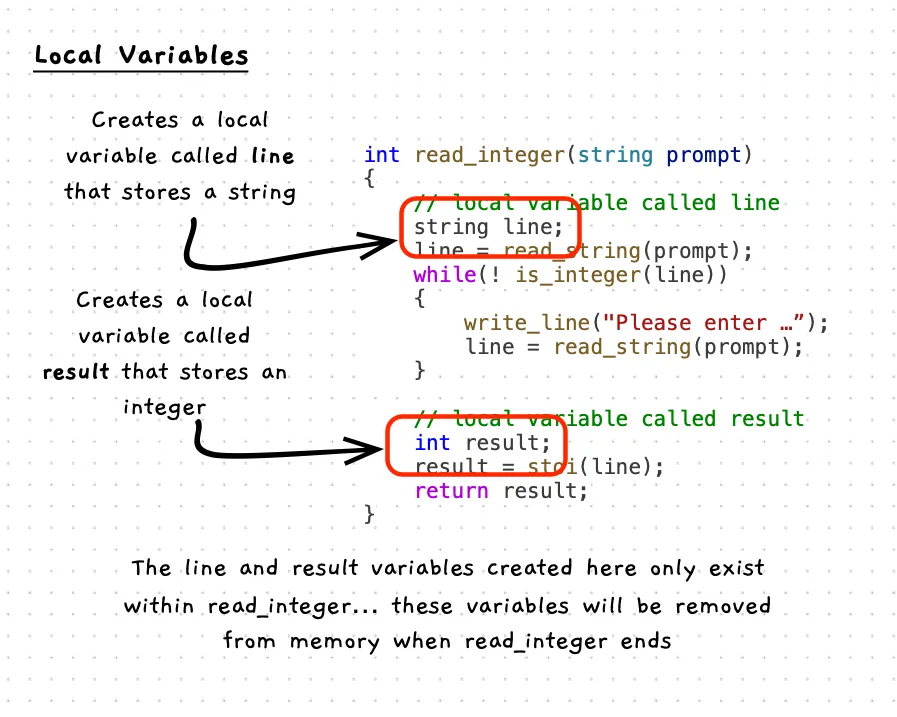
The following code has local variables within each function. Each local variable lives within the function it is created inside, can only be accessed by that functions code, and is removed from memory when the function ends.
You may notice that both read_string and read_integer have variables called result - these are different variables. Remember that each function or procedure is isolated from the others, so the things they create only exist within their scope.
#include "splashkit.h"
using std::stoi;
/*** Prompt the user to enter a string, and return the value to the caller.** @param prompt The message to show the user* @returns The data entered by the user*/string read_string(string prompt){ // Create a local variable called result string result;
write(prompt); result = read_line();
return result;}
/*** Prompt the user to enter an integer, and return the value to the caller.** @param prompt The message to show the user* @returns The data entered by the user*/int read_integer(string prompt){ // Create a local variable called line string line; line = read_string(prompt); while(! is_integer(line)) { write_line("Please enter a whole number"); line = read_string(prompt); }
// Create a local variable called result int result; result = stoi(line); return result;}
int main(){ write_line("Calling procedures is fun");
// Create a local variable called name string name; name = read_string("Enter your name: ");
// Create a local variable called number int number; number = read_integer("Enter your favourite number: "); //... return 0;}