Allocating an Array
You can also use malloc to give you space for more than one value, and then you can treat the pointer like an array.
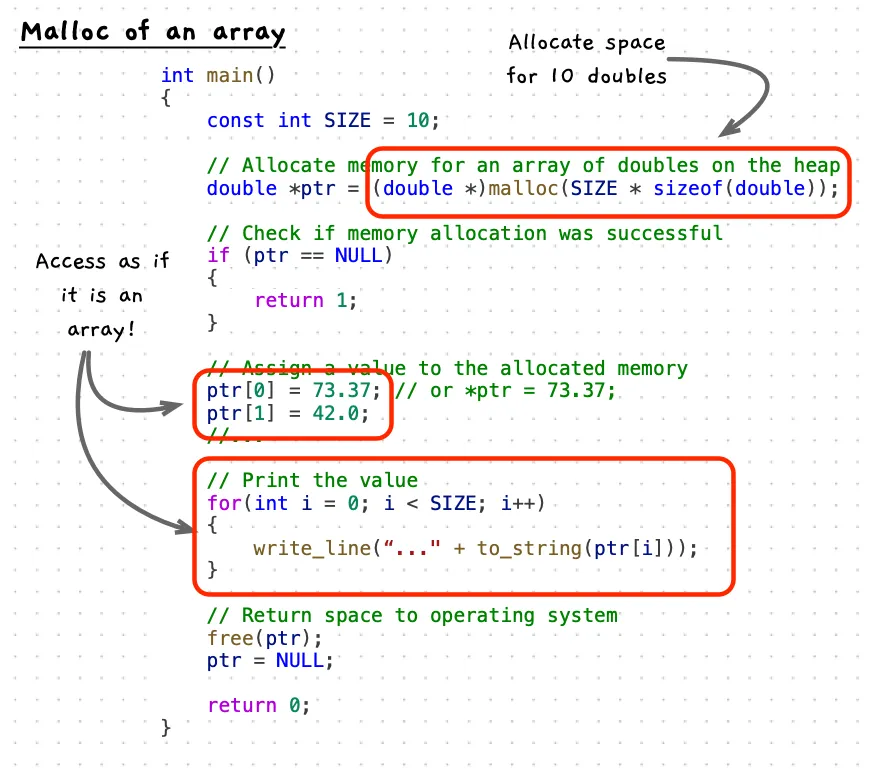
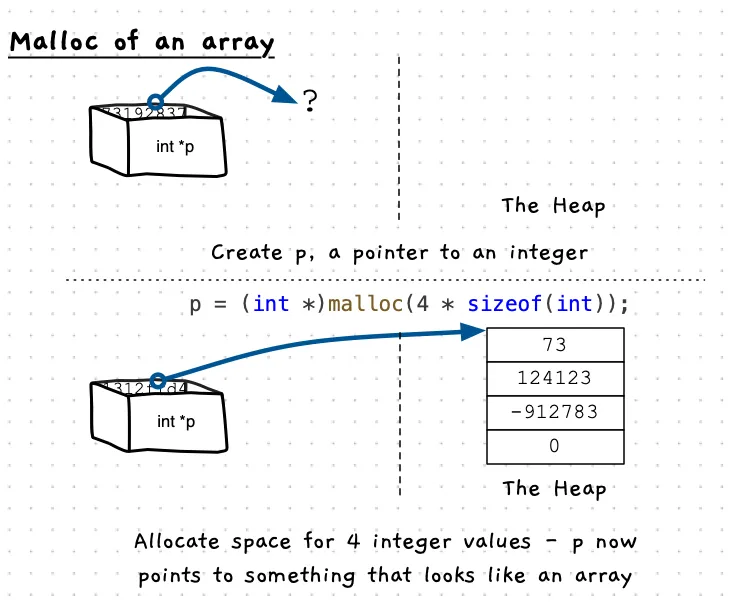
Example Code
The following code allocates space for an array of doubles, initialises some and then prints all values.
#include <stdlib.h>#include "splashkit.h"
using std::to_string;
int main(){ const int SIZE = 10;
// Allocate memory for an array of doubles on the heap double *ptr = (double *)malloc(SIZE * sizeof(double));
// Check if memory allocation was successful if (ptr == NULL) { write_line("Memory allocation failed"); return 1; }
// Assign a value to the allocated memory ptr[0] = 73.37; // or *ptr = 73.37; ptr[1] = 42.0; //...
// Print the value for(int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { write_line("Value at index " + to_string(i) + ": " + to_string(ptr[i])); }
// Free the allocated memory free(ptr); ptr = NULL;
return 0;}