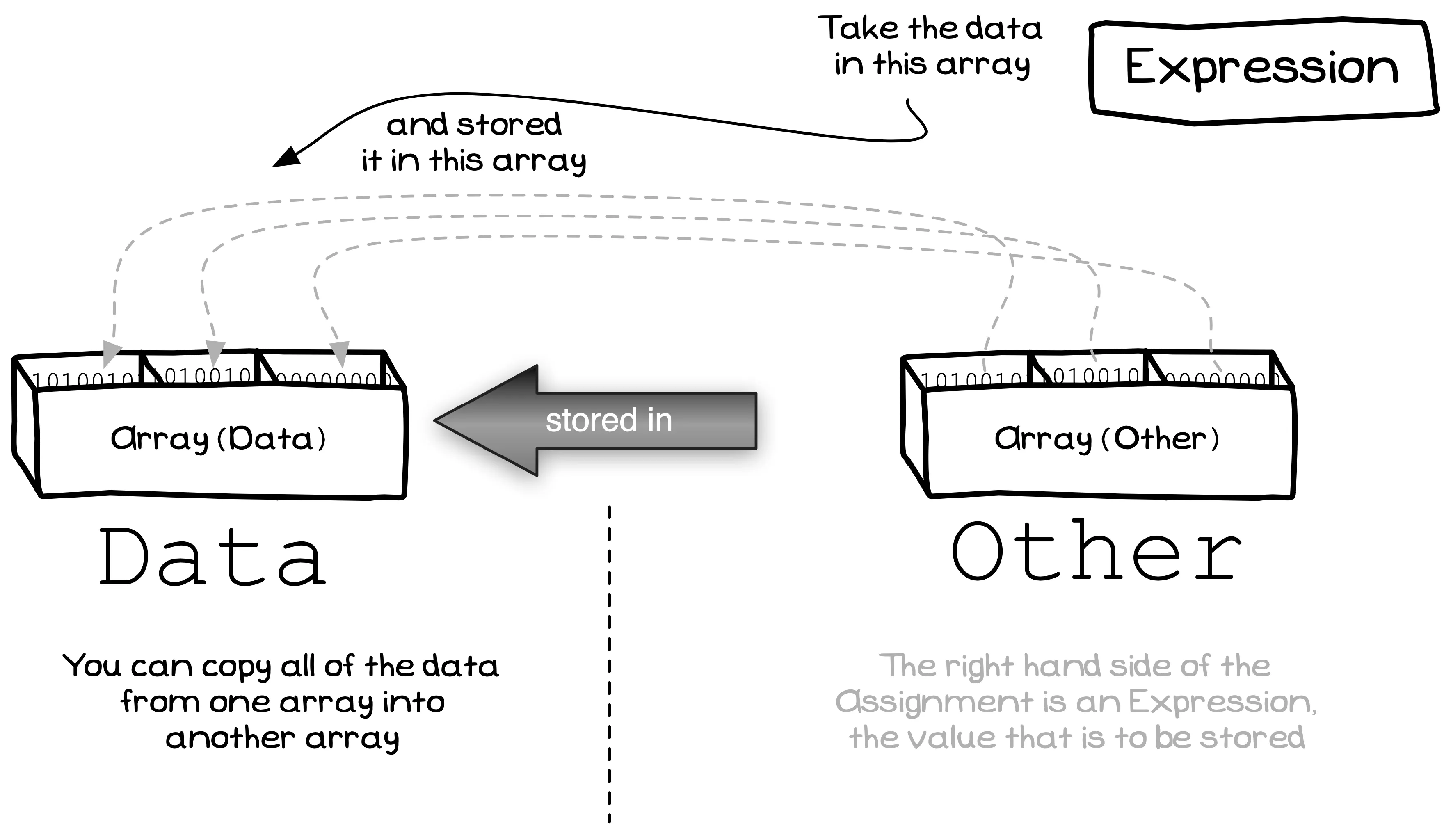
Copying an Array
Some languages allow you to copy the entire contents of an array into another array using a standard assignment statement, but often this is something that you need to take care of yourself.
You cannot use the assignment statement to copy arrays in C/C++. Instead, this can be achieved by manually copying the array yourself or by using the memcpy function.
The memcpy function copies a chunk of memory from one location to another.
Function: memcpyPrototype: void *memcpy(void *destination, const void *source, size_t num )Returns: (void *) the destination is returned, can be ignored.Parameters: - destination: The location where the data is copied to. - source: The data to copy. - num The number of bytes to copy.The destination and source are void pointers (void *) which is C’s way of saying “a pointer to anything”. You pass in the pointer to where to store the data (the left-hand side of an assignment normally), the source (the right-hand side), and the number of bytes to copy.
To determine the size of the data to copy, you use the sizeof operator. You can read more on this in the C++ reference site.
Operator: sizeofReturns: (size_t) the number of bytes for a typeParameter: a type or expressionThe following code demonstrates the use of memcpy and sizeof to copy one array into another.
#include <string.h>
int main(){ int data[3] = {1, 2, 3}; int other_data[3]; int more_data[3];
memcpy(other_data, data, 3 * sizeof(int)); memcpy(more_data, data, sizeof(data));
return 0;}