Array of Structs
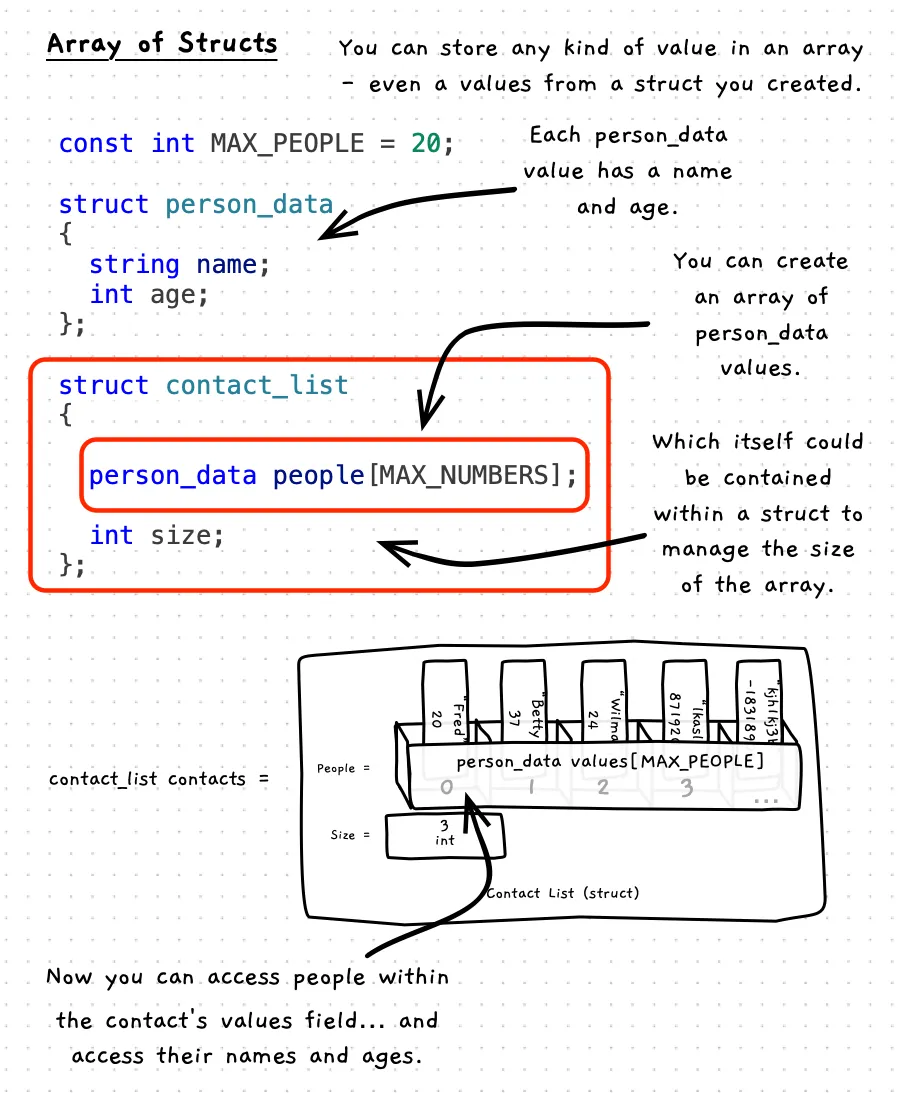
An array can contain any kind of data. So, you can have an array of a struct that you create. The following illustration shows an array of person_data values. This array is contained within a struct to manage the array, giving us a struct that contains an array that contains a different struct. With this flexibility you can start to model complex data, nesting data within other values as needed.
Example
#include <cstdlib>#include "splashkit.h"
using std::to_string;
const int MAX_PEOPLE = 20;
struct person_data{ string name; int age;};
struct contact_list{ // Here we have an array of people data values... person_data people[MAX_PEOPLE]; int size;};
void print_person(person_data &person){ write_line("Name: " + person.name + " Age: " + to_string(person.age));}
int main(){ // The contact list contains the array of people, and its current size contact_list contacts = {{}, 0};
// You can also create local variables that are arrays of structs. person_data other_people[MAX_PEOPLE];
// When you access 'people' each value is a struct contacts.people[0].name = "Fred"; // so we can access the name contacts.people[0].age = 20; // and we can access the age of any value
contacts.people[1].name = "Betty"; contacts.people[1].age = 37;
contacts.people[2].name = "Wilma"; contacts.people[2].age = 24;
contacts.size = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.size; i++) { // you can access each element as the struct data print_person(contacts.people[i]);
// or access fields directly write_line("Name: " + contacts.people[i].name + " Age: " + to_string(contacts.people[i].age)); }
return 0;}