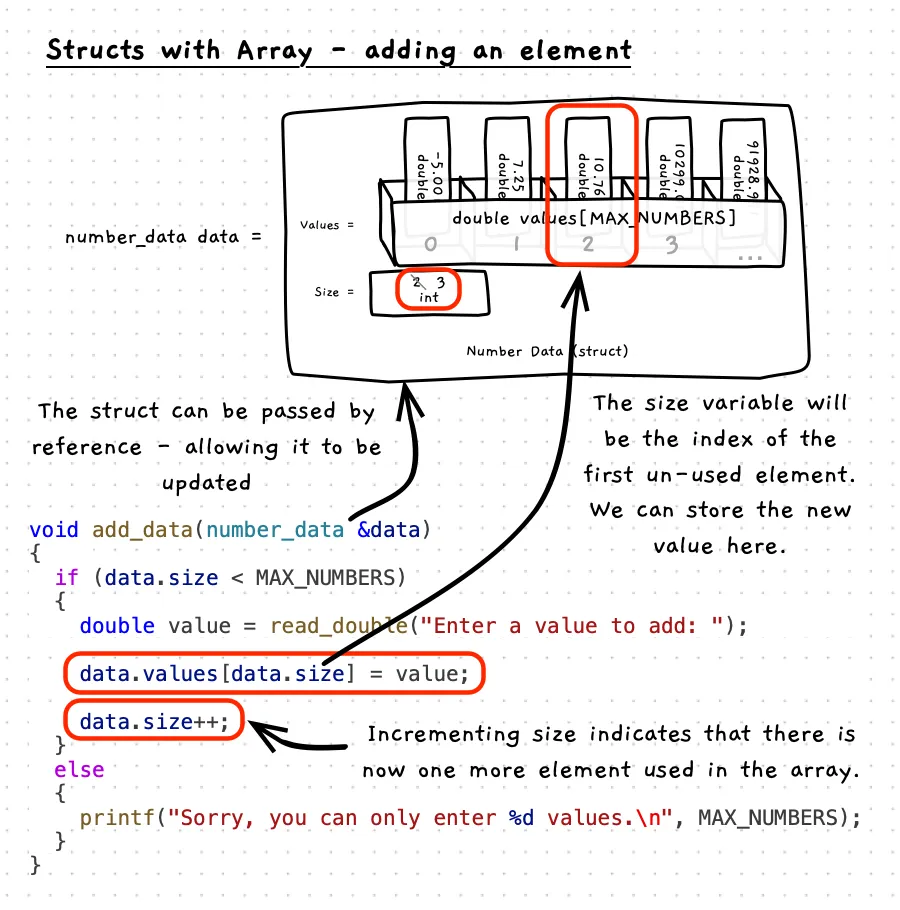
Adding Elements
Now we can change the size of the array, up to a certain maximum, we can think about how an element can be added to an existing array. The process for this will involve:
- Checking there is space
- Adding the new data to the first available element.
- Increasing the size value
This will then ensure that the new element is included in any subsequent processing.
Example
#include <cstdio>#include "utilities.h"
// The maximum number of values we can storeconst int MAX_NUMBERS = 20;
/** * The data structure to store the numbers * * @field values the array of values * @field size the number of values in the array - up to MAX_NUMBERS */struct number_data{ double values[MAX_NUMBERS]; int size;};
void add_data(number_data &data){ // Check that we have space. if (data.size < MAX_NUMBERS) { // Ensure this works if size is negative if (data.size < 0) { // It was negative, so set it to 0. data.size = 0; }
// Read the value in to the first available element double value = read_double("Enter a value to add: "); data.values[data.size] = value; // Increase the size data.size++; } else { // No space, so show an error printf("Sorry, you can only enter %d values.\n", MAX_NUMBERS); }}
int main(){ // Initialise struct with an empty array and a size of 0. number_data data = {{},0};
// We can add to the array a number of times add_data(data); add_data(data); add_data(data);
// Loop through printing all values for (int i = 0; i < data.size; i++) { printf("%lf\n", data.values[i]); }
return 0;}