Parameters
Procedures are useful for grouping code, but in most cases the instructions they contain need to be given values to work with. These values can be passed to the procedure using parameters. A parameter is a variable that has its value set by an argument in the procedure call. You have already seen how to provide values to functions and procedures when calling them, but now we will explore how to add and use parameters in our own functions and procedures.
As shown in the following image, you can picture parameters as variables that sit on the boundary of the function or procedure. Each parameter is a variable, which can be accessed in the function or procedure’s instructions.
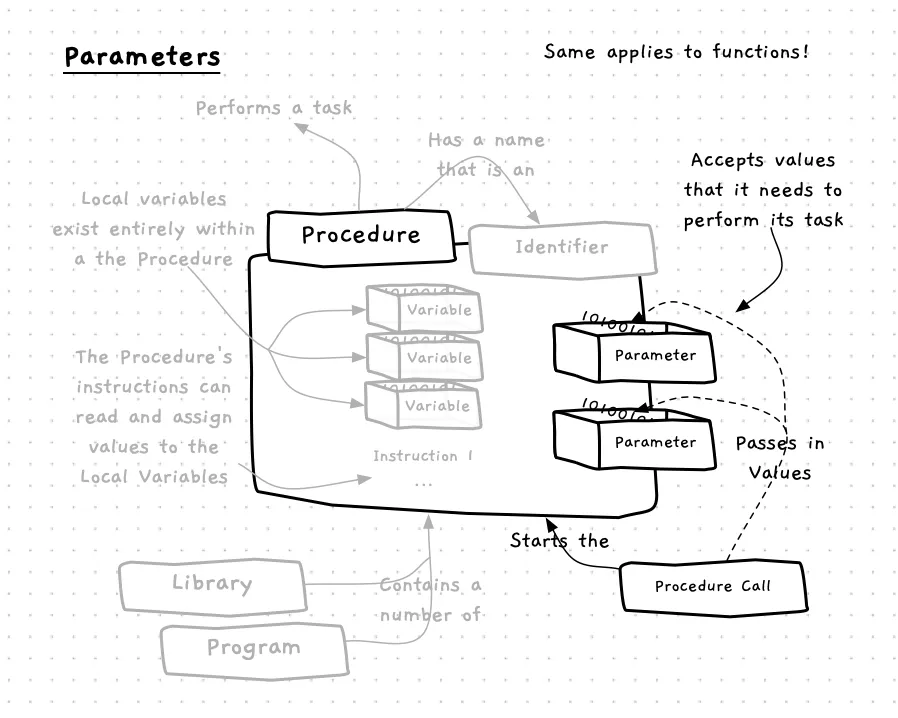
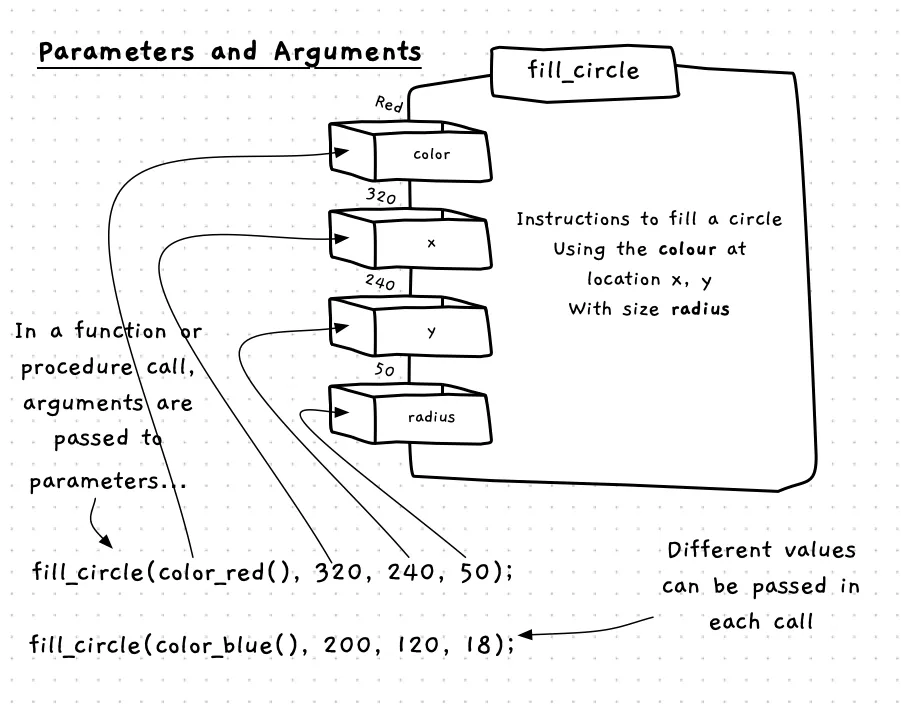
When a procedure is called, the arguments provide the values for the parameters. This allows the caller to give data to the function or procedure. The example below demonstrates this for with the fill_circle procedure. This has parameters for the color, position (x and y values), and radius for the circle. These are used in the procedure to draw the shape. During the call, you provide the values for these in the arguments, allowing the one function/procedure to draw any number of circles.
Parameters - when, why, and how
In most cases your functions and procedures will need to know things in order to perform their actions. Perhaps the easiest way to think about this is as if you were asked to do the task. If you were asked to put something in the bin, you would need to be told what to dispose of. In a program, this could be coded as a dispose procedure, where the thing to dispose would be the parameter.
As you start to create a function or procedure, think about what it will need to be told in order to perform its actions. Code these as parameters, and you can then pass the actual values to use as arguments.
Think about the different functions and procedure we have been calling already. When you call open_window you passed in arguments for the title, width, and height of the window. This means there are three parameters in this procedure, the first accepting the value for the title, the second the width, and the third the height. The open_window code uses these values when it creates the window you see appear on the screen.
In C/C++
Parameters are an optional addition to any function or procedure declaration. The syntax in both cases is the same — in between the declarations parentheses you write variable declarations (without initialisation), separated by commas. Each variable is a single parameter.
Examples
Procedures with parameters
The following code shows an example of a procedure with parameters.
using std::to_string;
void print_equation(int m, double x, int c){ double solution = m * x + c; write_line( to_string(m) + " x " + to_string(x) + " + " + to_string(c) + " = " + to_string(solution) );}
int main(){ print_equation(2, 5.1, 3); print_equation(7, 2.74, -8); return 0;}The print_equation procedure accepts three parameters: m, x, and c. This means that when print_equation is called, it must be passed three argument value. The first value will be passed to the m parameter, the second to x, and the third to c.
The swiper below explores how this code works.