Struct
You can create your own composite types using a struct. Each struct describes a type that is made up of fields. When you create a variable of this type is has space for each field, allowing you to access it as a whole or to access each field separately.
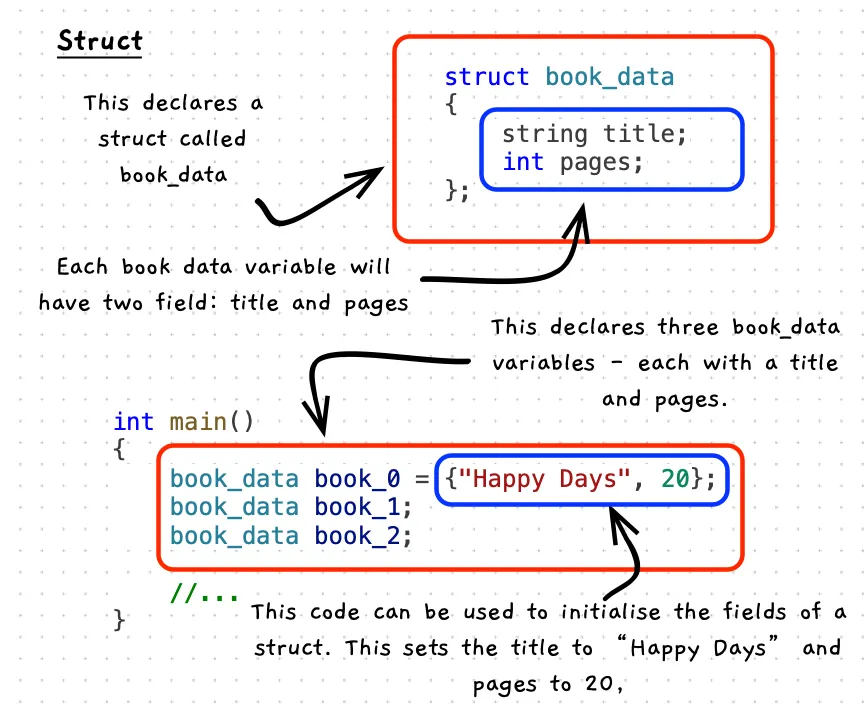
Annotated
book_data struct and example variablesExample
In this program we create a new book_data type. This means we can create and work with values that represent books within our program.
#include "splashkit.h"
// Access read_integer and read_string in utilities#include "utilities.h"
using std::to_string;
/** * Book data captures details for a single book. * * @field title the title of the book * @field pages the number of pages in the book */struct book_data{ string title; int pages;};
/** * Output details of a book to the terminal * * @param book the book to output */void print_book(book_data book){ // Access fields of the book to get details write_line(book.title + " (" + to_string(book.pages) + " pages)");}
/** * Read in the details of the book from the terminal * * @param prompt a message to show the user when they start * to enter the book data * @return a book populated with the data the user provided */book_data read_book(string prompt){ // Create a book variable, and initialise it book_data result = {"", 0};
write_line(prompt);
// Store data into result's title result.title = read_string("Enter book title: ");
// Store data into result's pages result.pages = read_integer("Enter number of pages: ");
return result;}
int main(){ // Initialise book_0 book_data book_0 = {"Happy Days", 20}; book_data book_1; book_data book_2;
// Read in book data, and store in variables book_1 = read_book("Enter book 1 details."); book_2 = read_book("Enter book 2 details.");
// Pass in the book data to have it printed print_book(book_0); print_book(book_1); print_book(book_2);
return 0;}